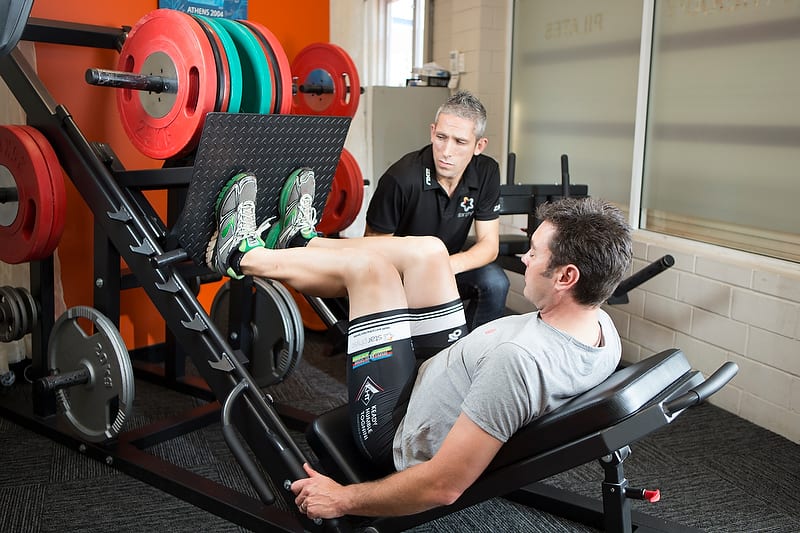
Physiotherapy as an initial treatment for Femoroacetabular impingement. Review of Literature.
Dr James Debenham (PhD), Star Physio Research Director reviews physiotherapy treatment for a common hip complaint seen in athletes called femoroacetabular impingement. Have you been told you might have FAI, or do you have pain in the front of the hip? Read on!!!
Hoit, G., et al. (2019). “Physiotherapy as an Initial Treatment Option for Femoroacetabular Impingement: A Systematic Review of the Literature and Meta-analysis of 5 Randomized Controlled Trials.” Am J Sports Med 1
What is femoroacetabular impingement (FAI):
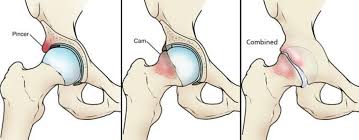
Examples of anterior hip impingement.
So femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) is a common source of hip pain that affects active young adults. Put simply, it presents as pain felt in the front of the hip (groin region), that occurs when the hip joint gets compressed at the front during hip flexion activities.
For this reason, it affects athletes who do repetitive or vigorous hip flexion sports (think cyclists, hill runners, footballer, and hockey players). When mild it is felt as a “tightness in the front of the hip” which is commonly misinterpreted as a “tight hip flexor”. When more severe, the pain becomes sharp and catching and very limiting to sports participation.
What did the study show?
Whilst Physiotherapy is considered the mainstay of care for FAI, the evidence regarding different physiotherapy practices is actually not well understood. In the paper here by Hoit et al, the authors systematically collected and synthesized the best available evidence to establish the utility of physiotherapy in the management of FAI. This study identified a total of 5 randomized controlled trials, which all compared different physiotherapy protocols such as core strengthening, active strengthening, and passive modalities (e.g. stretching, massage, dry needling, etc.). They also explored the concept of supervised vs. un-supervised physiotherapy.
The authors were able to do this thing called a “meta-analysis”, which pools all the findings from these studies to establish group-effectiveness from all the studies combined; what helps and by how much? This analysis collectively demonstrated improved outcomes with physiotherapy.
Looking a little closer, they found that core strengthening and active strengthening, when supervised by a physio resulted in statistically significant improvements in outcomes. Interestingly though, when exercise is unsupervised, or only passive treatments are applied, the treatments were ineffective.
My interpretations:
This was a well conducted, vigorous trial, so we should trust the findings. Whilst the findings were consistent, they were based on only 5 RCT’s (that isn’t many), so it is possible that future evidence may prompt us to modify our thinking. However, the findings clearly suggest that if you have FAI, then strengthening should a key ingredient of your treatment.
Furthermore, this treatment does require supervision to be effective. To add my clinical interpretation to this, that doesn’t necessarily mean that every single session needs to be supervised, but there needs to be regular check-ins (this could be anywhere between weekly and monthly depending on the circumstances), to ensure that the exercise selection, dose, progression and execution are all perfect. For my patients receiving strengthening programmes (and almost all do), these regular catch-ups always end up with significant refinements being made and represent high-value interactions.
Unfortunately, many health professionals do not keep up with research and evidence, and also do not understand the science of strength and conditioning, continuing to prescribe exercises that do not challenge the system enough to give the necessary strength gains to get improvement of symptoms.
Strengthening is highly effective, but only when done correctly.

Dr James Debenham is an expert in rehabilitation of hip pain at Star Physio.
Finally, the study reinforces the notion that passive treatments should be viewed with caution in the management of this condition. Passive treatments can add value certainly, and result in alterations in symptoms, but it should not represent the primary ingredient of your management plan. When supplementing a high quality well-supervised strengthening programme, massage, manual therapy and dry needling can certainly add value, but please do not expect this alone to result in a successful long-term outcome and ask questions of your health professional of this is all that they are offering!
If you have anterior of front of hip pain, get in touch with James and the expert team at Star Physio. As we say, “not all physiotherapists are the same”!

Tips for Handling Long Rides
About to set off on your first long ride? Long rides are one of the true joys of cycling, but it's important to take your time before throwing yourself into the deep end. To help you feel more prepared, we’ve put together the ultimate guide to handling long bike...

4 Reasons To Take Up Cycling
People all over the world love cycling! It is a good form of regular exercise as well as an alternative option for the daily commute. Cycling has many physical and mental health benefits for individuals, as well as being better for the environment, easy to do...
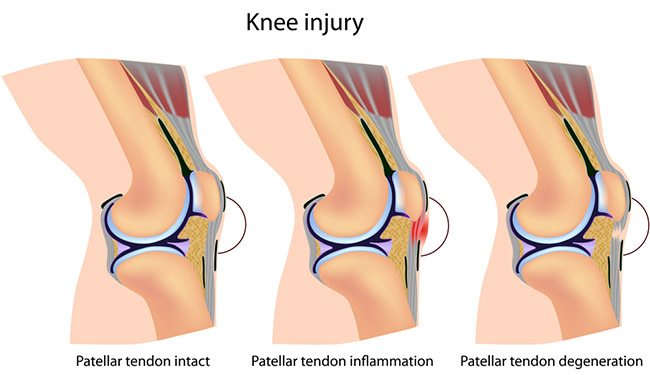
Jumper’s Knee – What Is It and How Can I Fix It?
The team at Star Physio has seen a lot of clients with jumper's knee over the years. We shed some light on this overuse injury, common among volleyball and basketball players. What is Jumper’s Knee? Patellar tendinopathy, commonly known as jumper’s knee, is an overuse...

Good Habits for Eliminating Chronic Back Pain
At some point or another, almost everyone experiences acute back pain in their lifetime. It’s not a pleasant experience, but the good news is that in most instances, back pain can be relieved quickly with the help of a physiotherapist who can also help you prevent...

